10. 3D printing
3D printing uses computer-aided design to create three-dimensional objects by layering materials like plastics, composites or biomaterials. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing revolutionises production by enabling rapid prototyping and customised manufacturing, reducing waste and costs.
Overall, these technologies represent a revolution due to their exponential growth and potentially profound impact on our lives.
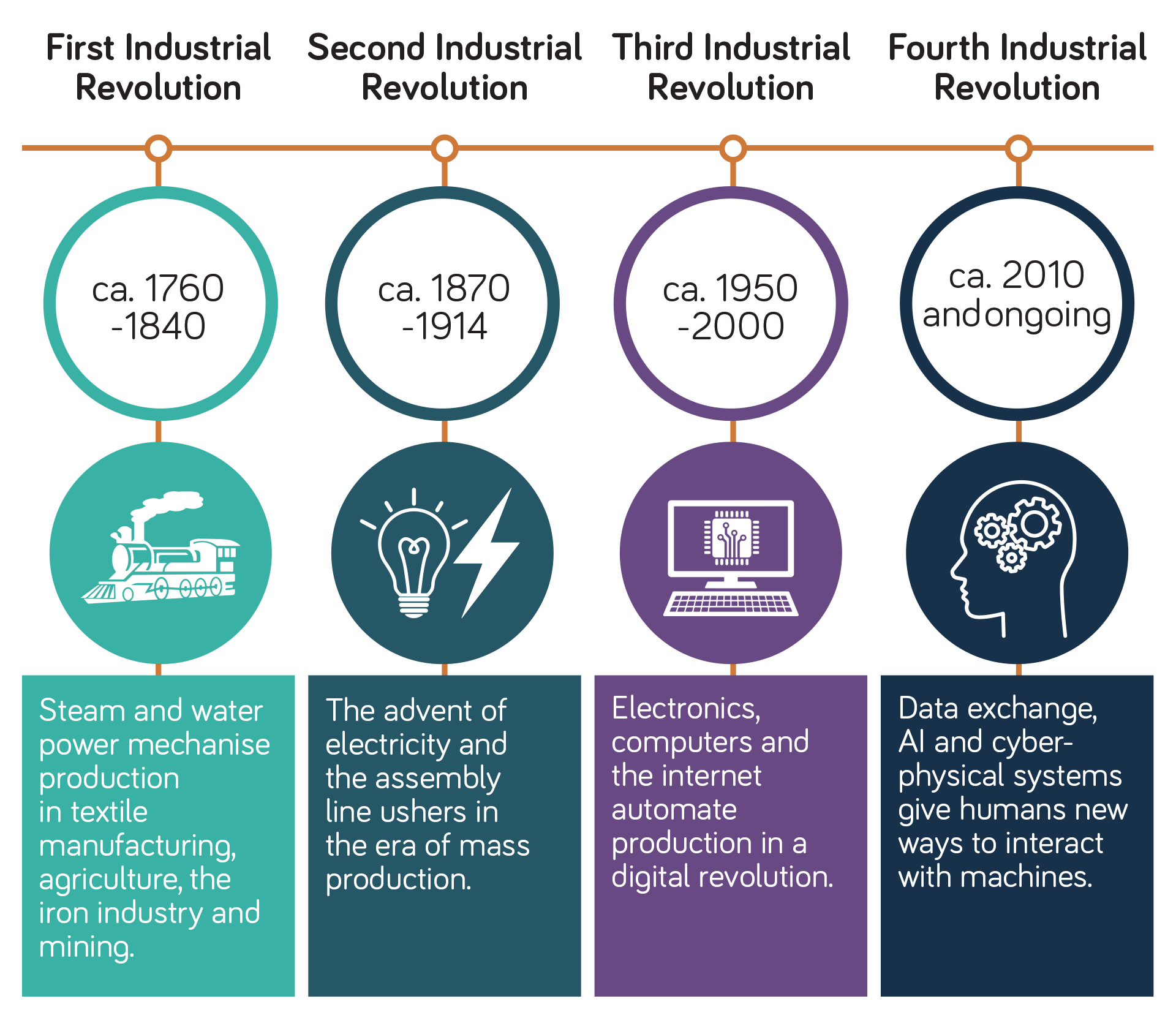
Impacts of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
As 4IR technologies advance, they’re expected to transform the economy, society, government and environment of countries worldwide.
Economy
First, integrating tech like AI, robotics and automation enables businesses to boost productivity and efficiency. This can lead to higher production, faster product innovation, enhanced customer service and reduced costs.
Second, 4IR is set to drive innovation in products and services, transforming existing industries or creating new business models. Advanced manufacturing techniques will allow greater personalisation of products and services.
Third, these technologies are set to displace some traditional manufacturing and routine white-collar jobs. However, they’ll also create new jobs in high-tech industries, data analysis and cybersecurity.
Society
To meet the demands of this new economy, education will have to adapt. Schools and higher education must focus on STEM education and lifelong learning to enable individuals for future jobs.
All the more so because we’ll live longer. Advances in health care, personalised medicine and smart infrastructure will likely improve older people's life expectancy and quality of life.
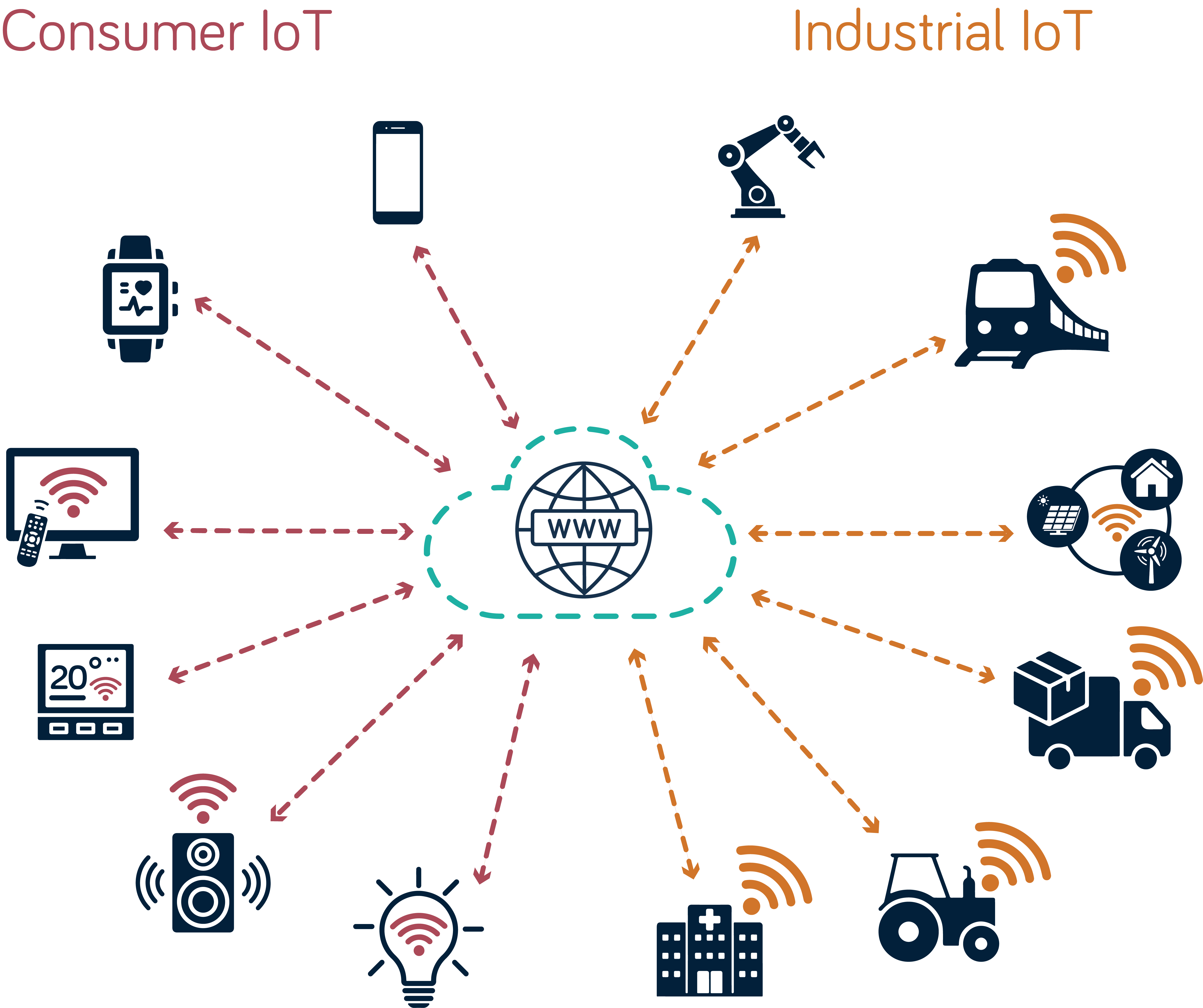
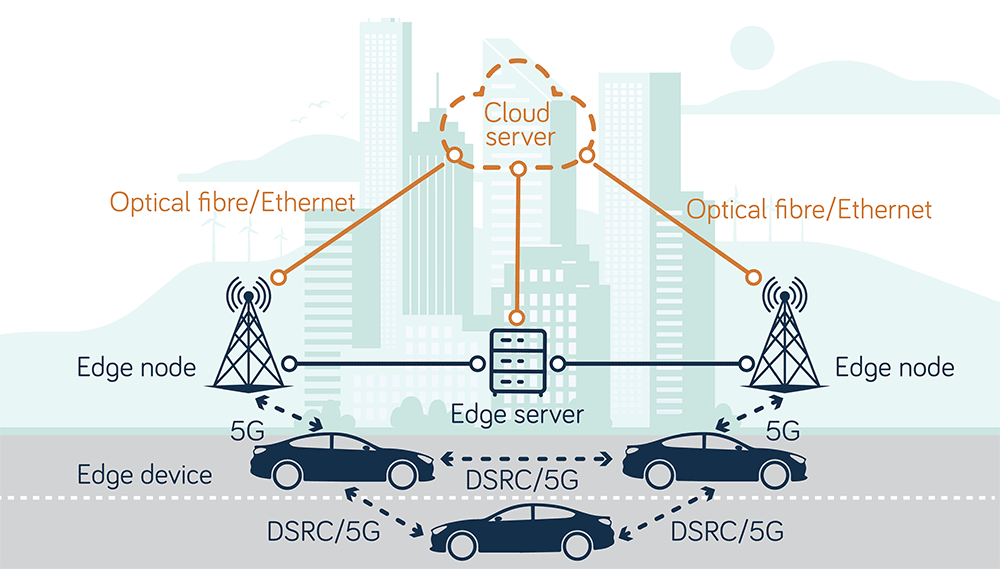
In addition, the proliferation of internet-connected mobile devices and the rise of IoT gives us unprecedented connectivity. This enables near real-time data exchange globally, fostering collaboration and competition.
However, access to advanced technologies varies across communities and countries. Owners and investors in new technologies are poised to gain significant wealth. As a result, the rapid pace of technological change could exacerbate existing wealth and digital divides.
Government
Governments will have new ways of interacting with citizens to address these challenges. For example, e-government services and smart cities are already used in the UK to enhance public services.
On the other hand, emerging technologies can threaten fundamental freedoms. Across the globe, dictators find new ways to monitor and control their populations. And rapidly evolving technological innovation increases the risk of war and the means to wage it.
Environment
On the positive side, renewable energy, smart manufacturing and new sustainable practices can mitigate environmental impacts. Together with new technologies like carbon emissions management, they can help us tackle climate change.
Yet the increase in energy consumption from AI and cloud computing, electronic waste and the depletion of resources could degrade the environment if not managed properly – one of several challenges the revolution poses.
Challenges of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
While 4IR is set to bring enormous benefits, its blurring of the digital, physical and biological spheres entails several risks. Here are some key challenges.
First, the data explosion fuelled by industries like cloud computing, AI, and IoT raises data privacy and security concerns. In a hyperconnected world, how can we protect user privacy? How can we defend complex, interconnected systems against cyberattacks?
Second, the rapid rise of AI, genetic engineering, biotech, autonomous vehicles and robots pose thorny ethical questions. For example, how can we remove bias from AI decision-making? How can we control biohacking and prevent designer babies? How can we stop autonomous robots from getting out of control?
Third, the socioeconomic impacts above could lead to income inequalities, business bankruptcies, unemployment and even social unrest. How can governments and individuals adapt?
Overall, how can we effectively regulate 4IR technologies? The regulation of new technology often fails to keep up with the pace of innovation, and rules and enforcement differ around the world.
Adapting to the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Meeting the challenges of 4IR will require collective, global efforts across various industries.
First, governments should work with businesses, academia and wider society to regulate new fields like AI and biotechnology. We need timely international regulation of 4IR technologies to promote their benefits while mitigating risks.
As individuals, we need to get used to flexible careers and continuous learning. With the rapid pace of change, education will likely become a lifelong process as we adapt to evolving tech.
For businesses, new technologies mean new opportunities and new threats. To meet these challenges, companies will need to:
- Prioritise digital transformation: Invest in digital infrastructure and technologies like AI and IoT to enhance products, operational efficiency and customer service.
- Train employees: Provide continuous learning for staff to work with evolving technologies.
- Adopt Agile working: Introduce methodologies to enhance flexibility and foster a culture of innovation.
- Improve data management: Collect and analyse data to improve business insights and decision-making.
- Bolster cybersecurity: Protect sensitive data from increasing cyber threats.
We can’t predict the future, but one thing seems certain: connectivity will be crucial to compete in this new world.
At Neos Networks, we deliver scalable, high capacity connectivity for UK businesses nationwide. If you’re looking to connect your business for the future, contact us. We’ll be happy to design a network for your business, however the revolution unfolds.