- Home
- Resources
- Blog
- Home
- Business General
- What is artificial intelligence (AI) in networking?
What is artificial intelligence (AI) in networking?
- Neos Networks
- Business General ,

Learn how AI is set to transform how we manage large, increasingly complex IT networks.
- What is artificial intelligence (AI) in networking?
- Why use AI in networking?
- 5 ways to use AI in networking
- How AI can enhance network security
- AIOps and the future of networking
- The challenge of AI in networking
What is artificial intelligence (AI) in networking?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a set of technologies that can reason and learn to solve problems or perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence. For network service providers, that means new ways to make their networks more efficient, resilient and secure.
A range of AI technologies can be harnessed to help run complex IT networks, including the following:
- Machine learning (ML) uses algorithms trained on data to predict outcomes and perform specific tasks.
- Deep learning (DL), a subfield of ML, uses artificial neural networks to mimic the human brain.
- Generative AI (GenAI) uses DL models to generate text, images, video or other media that mimic human-generated content.
- Natural language processing (NLP) enables computers to understand spoken and written language.
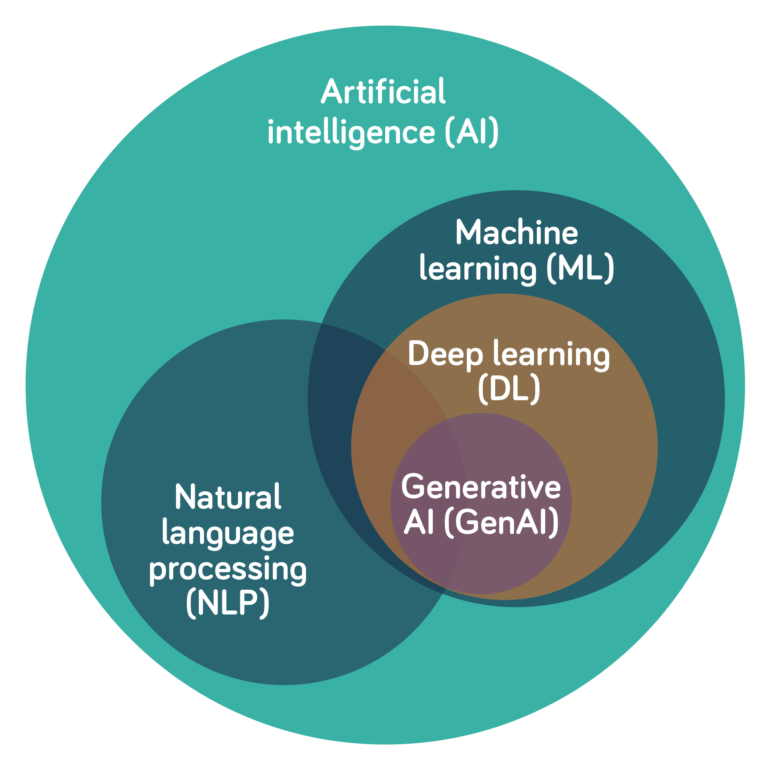
AI technologies for networking
While it’s still early days for AI in networking, these and related AI technologies are set to reshape how we design and operate growing IT networks.
Why use AI in networking?
The rise of AI, 5G, the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing are fuelling an explosion of data. Meanwhile, networks are becoming larger and more complex.
They’re also becoming increasingly complex to manage, as recent outages at Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure have shown. Cloud service downtime is often attributed to network issues, which can be challenging to diagnose and remedy quickly.
That’s where AI comes in. By analysing vast quantities of historical and real-time telemetry data, AI can help in all aspects of network management, from provisioning and deployment to maintenance, troubleshooting and optimisation.
First, AI can free up network administrators from routine, time-consuming jobs, allowing them to focus on higher value, strategic tasks. Second, it can identify network trends and anomalies that the most experienced engineer would find difficult or impossible to spot using manual processes.
In short, implementing AI in networks has the potential to:
- Boost network efficiency and reliability
- Simplify network troubleshooting and maintenance
- Increase network resilience and security
- Reduce set-up and maintenance costs
- Enhance user experience
So how can AI deliver these benefits and transform how we manage large networks?
5 ways to use AI in networking
Here are some potential AI-enabled solutions for networking, though most are yet to be fully developed or widely adopted.

1. AI for network optimisation
With the ability to monitor networks in real time, AI can dynamically allocate resources like bandwidth, processing power and storage to meet changing demands. In this way, AI can adjust Quality of Service (QoS) configurations, load balancing and dynamic routing to optimise network performance.
2. AI for network troubleshooting
AI can monitor complex networks to quickly identify the root cause of issues, speeding up problem resolution. Sifting through reams of data in minutes, AI can help rapidly identify the network component at fault, eliminating false positives. And AI-powered self-healing systems allow some issues to be resolved without an engineer’s intervention.

3. AI for predictive maintenance
Since AI can compare historical and current network patterns, it can detect minor abnormalities in performance before they develop into major faults. Similarly, with predictions based on historical data, AI can model the network to prevent network deterioration or outages in the future.

4. AI for network scalability
Automation enhanced by machine learning allows network providers to provision and deploy network resources automatically. In other words, AI enables you to dynamically scale network resources based on real-time and predicted demand.

5. AI for customer experience
Besides improving overall network performance and reliability, AI can significantly enhance the customer experience by providing intelligent, targeted solutions. For example, it can predict user behaviour to dynamically adjust bandwidth and minimise network disruptions. Meanwhile, chatbots and virtual assistants can give customers personalised, context-aware support 24/7.
Yet AI isn’t only useful to enhance efficiency and user experience. Its ability to intelligently analyse data in real time also makes it an excellent tool for network security.
How AI can enhance network security
AI-powered security solutions can monitor network operations for security issues and alert network engineers or automate incident responses.
Threat detection
Monitoring historical data and traffic data in real time, AI-powered systems can identify abnormalities or known patterns that may indicate a potential cyberattack. For example, it has the potential to detect zero-day attacks, which are usually missed by traditional signature-based detection methods.
Automated response
Once a potential threat is detected, AI-enabled risk analysis can triage and automate incident responses to prevent escalation, contain damage or enable rapid recovery. For instance, it can update firewalls, block malicious traffic or “clean” infected files.
Device tracking
AI can also help with one of the most demanding network security challenges – tracking connected devices. As IoT devices proliferate, machine learning can help identify, categorise and manage them, checking for potential vulnerabilities and outdated software.
Policy automation
Similarly, AI can create and deploy security policies as required. For example, it can allow or deny access to specific devices, users or apps, dynamically responding to changes on the network.
Whatever the security issue, AI has the potential to speed up human responses or deploy fast, automated self-healing, countering a potential threat before it escalates.
AIOps and the future of networking
Despite the enormous potential benefits, the AI-enabled solutions outlined above are yet to be widely implemented in the industry. So-called AIOps – artificial intelligence for IT operations – is still in its infancy.
However, as machine learning and other AI technologies evolve at breakneck speed, expect to see AI’s role switch from cameo to hero. From network design and deployment to maintenance and customer service, AI will become integral to future network operations.
One emerging trend is to apply AI to streamline network services. Machine learning can enhance zero-touch provisioning and enable end-to-end network automation.
Another is harnessing AI for software-defined networking (SDN). For instance, as more IoT devices come online daily, engineers can use AI-enhanced SDNs to design and control scalable, secure industrial IoT networks.
The challenge of AI in networking
Estimated at around $8.3 billion in 2022, the global AIOps platform market is expected to reach about $80 billion by 2032. Yet AI in networking faces several challenges before it becomes mainstream, such as:
- Complexity and integration: Today’s networks are increasingly complex with multiple interlinked components, data sources and interfaces. Integrating AI solutions requires rethinking pre-existing networks to allow for this complexity.
- Data integrity and security: AI relies on maintaining and processing vast quantities of high-quality data. Any emerging AI networking solutions must ensure data integrity, security and privacy by design.
- Interoperability and open standards: Data from multi-vendor networks remains challenging because the data format and syntax may differ by vendor. In future, the evolution of open standards, like Open RAN, should help meet this challenge.
- Skills gap and retraining: Integrating AI in networking will require a change in working culture for network engineers. As AI technologies evolve, they’ll need to learn new skills and working methods to deploy and maintain AI-powered networks.
In short, AI won’t transform networking overnight. A world of automated, software-defined, self-healing, self-defending networks is still some way off.
You might also like
We can connect you anywhere in the UK
Discover our network reach
Great news!
"[poscode]" can be reached with our
expanded network
Speak to a representatitive to discuss your options
Contact usLearn about our prices using our online tool, LIVEQUOTE
View LIVEQUOTESorry
"[poscode]" can not be reached with our
expanded network
Speak to a representatitive to discuss your options
Contact usLearn about our prices using our online tool, LIVEQUOTE
View LIVEQUOTE