Get ultrafast, low latency Optical Wavelengths
What is optical networking?
Optical networking is a data-transfer technology that uses pulses of light to transmit data. Instead of electrical signals travelling over copper wires, data is carried as optical signals through fibre optic cables. This delivers far higher bandwidth than traditional copper-wire networks and allows data to be transmitted over extremely long distances.
Light travelling in a fibre optic cable: the light reflects at the core/cladding interface, a process known as total internal reflection

Optical fibre underpins modern IT networks, from high-bandwidth enterprise links to backbone networks, data centre interconnects (DCI) and 5G mobile backhaul. Starting at 10Gbps for standard enterprise needs, optical networks scale up to 100Gbps or 400Gbps for DCI and backbone networks, with hyperscalers now transitioning to 800Gbps and 1.6Tbps.
From local enterprise and metro networks to national and international links, optical networking forms the backbone of today’s internet and telecoms infrastructure.
How do optical networks work?
In simple terms, network equipment converts electrical data into optical signals, which are sent as pulses of light through fibre cables. At the far end, receivers convert the optical signal back into an electrical signal for processing.
To increase capacity, optical networks use Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), most commonly Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM). DWDM allows multiple data streams to travel simultaneously over a single fibre, each carried on a different optical wavelength (colour of light). At one end, a multiplexer combines these wavelengths. At the receiving end, a demultiplexer separates them into individual data streams.
Over long distances, light signals gradually lose power and can become unreadable. To prevent this, optical amplifiers are widely used to amplify many DWDM channels simultaneously, extending reach between regeneration points.
To steer the signal, reconfigurable optical add‑drop multiplexers (ROADMs) can direct any wavelength to any output port. This means you can remotely add or drop signals, or allow them to pass through, at different sites. So you can create a flexible, mesh-based optical network without manually reconfiguring intermediate nodes.
For longer distances and higher capacities, optical networks rely on coherent optics combined with digital signal processing (DSP). By encoding and recovering more information from each wavelength, these technologies maximise both the reach and efficiency of DWDM networks.
Finally, Optical Transport Network (OTN) is commonly used at the transport layer. Standardised by ITU-T G.709, OTN “wraps” different types of traffic (IP, Ethernet, etc) into a managed frame, improving resilience and efficiency for long-distance transport.
Let’s look at some of the key components optical networks rely on.
Optical networking components
Optical fibre cables
An optical fibre cable is constructed from bundles of individual optical fibres. Each one has a core, typically made of glass, through which the light travels. Wrapped around the core is glass or plastic cladding, which prevents the light from escaping. Outer coatings protect the cable from physical damage.
Cross-section of a fibre optic cable

Most modern networks use single-mode fibre, which supports extremely high-bandwidth, long-distance transmission with low attenuation (signal loss). For short-distance connections, such as within a data centre building, thicker multi-mode cables are used.
Transmitters and receivers (transceivers)
Transmitters use a laser or LED light source to convert the electrical signals into light pulses to send data. At the receiving end, a photodiode receiver converts the signals back into electrical signals. Today, the standard solution is to use transceivers, a compact network device combining both functions: sending and receiving data.
Multiplexers and demultiplexers
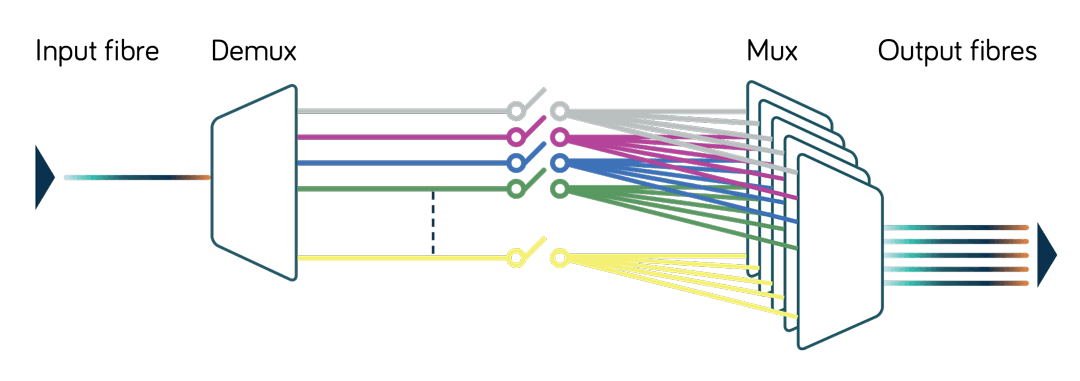
To expand network capacity, multiplexers (also known as muxes) combine multiple optical signals onto a single fibre. At the destination, demultiplexers (demuxes) separate them again. A vital component in DWDM and CWDM networks, they enable a dramatic increase in the capacity of existing fibre infrastructure without laying additional cables.
ROADMs
In modern DWDM networks, advanced multiplexers called ROADMs dynamically manage multiple wavelengths to enable flexible routing and rapid reconfiguration. Within a ROADM, wavelength selective switches (WSS) can switch incoming optical signals to different output ports based on their wavelength. This allows you to reconfigure optical paths as needed remotely.
ROADM WSS basic function
Optical amplifiers
As wavelengths degrade over long distances, amplifiers can be used to boost the optical signal without converting it back into electrical form. The most commonly used are erbium‑doped fibre amplifiers (EDFAs), which are typically placed every 70-100km on the network. Together with coherent transceivers and ROADMs, amplification enables multi‑span links from hundreds to thousands of kilometres.
Optical fibre vs copper networks
By using light rather than electrical signals, fibre networks provide higher bandwidth and lower latency over longer distances than traditional copper-based networks. Here’s a summary of how they differ.
Optical fibre vs copper networks
| Optical fibre | Copper | |
| Transmission | Light signals | Electrical signals |
| Bandwidth | Commonly 10/40/100/400Gbps per link, with aggregate capacity scaling to multiple terabits per second | Typically up to 10Gbps over twisted-pair (Cat6A) cabling; higher using very short direct-attach copper (DAC) cabling |
| Distance | Up to 70-100km per span on single-mode fibre without amplification; hundreds to thousands of kilometres with multi-span amplification | Up to around 100m at rated speeds for twisted-pair Ethernet; DAC links are limited to a few metres |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference | Susceptible to EMI and radio frequency interference |
| Latency | Consistently low latency over long distances due to optical amplification and fewer active regenerations | Increases over long distances because electrical signals need more frequent regeneration |
| Security | No electromagnetic signals, so interception is significantly more difficult | Electromagnetic signals can potentially be intercepted, so tapping is easier |
| Uses | High capacity, long‑distance connectivity such as access, metro and backbone networks, data centre interconnect and mobile backhaul | Short‑distance connectivity such as Ethernet LANs, legacy access networks and device connections |
Benefits of optical networks
Optical fibre networks offer several advantages for your business, particularly compared to traditional copper-based networks. Benefits include:
- High capacity: Delivers bandwidths from 10Gbps up to 400/800Gbps, with cutting-edge coherent optics now enabling 1.6Tbps per wavelength.
- Low latency: Consistently low or ultra-low latency supports real-time applications like cloud services, AI, 5G and IoT.
- Easy scalability: Quickly scale capacity by adding new wavelengths through DWDM.
- Enhanced security: Light transmission is harder to intercept than electrical signals, improving data confidentiality.
- Long-term cost: Wavelength-based scaling and reduced maintenance can deliver lower long-term operational costs
Despite the advantages, choosing the right optical architecture for your organisation can be challenging. Let’s consider the different types of optical networks.
Types of optical networks
Optical fibre networks can be broadly classified by their scale and the technologies they use. Among the most common are:
- Long-haul backbone networks: From nationwide links to international subsea cables, long-haul optical networks form the backbone of global communications. Typically operated by wholesale carriers and hyperscalers, they use DWDM, coherent optics and amplification to maintain high bandwidths over very long distances.
- Metro networks: Metro networks interconnect points of presence (PoPs) in cities or large urban regions, aggregating traffic between long-haul and access layers. Increasingly DWDM-based, metro networks often use Metro Ethernet and cover distances around 10-100km or more.
- Data centre interconnect (DCI): DCI links connect data centres, from short cross‑campus connections to wider metro or regional routes. Optimised for high bandwidth, low latency and reliability, they often use DWDM and high-speed Ethernet (100-800Gbps). Data centre operators may opt for Dark Fibre for maximum control or managed optical wavelengths for simpler scaling.
- Access networks: Also known as the last mile, access networks connect end users or subscribers to their service provider’s core network. They may be active optical networks (AONs), which use powered equipment and deliver dedicated point-to-point links. In the UK, examples include Openreach EAD and OSA tails for Ethernet and Optical Wavelengths. In contrast, passive optical networks (PONs) provide point-to-multipoint links to multiple subscribers, such as fibre-to-the-premises business broadband.
The above network layers aren’t mutually exclusive. Organisations often use more than one. If you’re considering high capacity optical connectivity, you’ll need to choose the right service model for your business.
Providers typically offer a range of options, depending on how much control you want over your network:
- Wavelength services: A fully managed optical service, like our Optical Wavelengths, where the provider delivers a single wavelength with a fixed capacity (e.g. 10Gbps, 100Gbps or 400Gbps). You don’t manage any optical equipment – just plug in and go.
- Spectrum services: You lease a block of optical spectrum (e.g. 75GHz) and can light it with your own transponders and DWDM line system equipment (or use the provider’s equipment). This gives you more control than a wavelength service with less complexity than managing an entire fibre. It can be a cost-effective stepping stone to Dark Fibre.
- Managed Optical Fibre Networks (MOFN): Like Spectrum, either you or the provider owns and manages the DWDM line system and transponders, depending on the setup. However, the provider typically manages the service, network operations and maintenance.
- Dark Fibre: You lease the entire fibre strand and manage everything end to end, including the optical equipment and signal transmission. It gives you maximum control with almost limitless scalability.
When choosing your model, you’ll need to consider your current and long-term use cases.
Optical networking use cases
Optical connectivity plays a critical role in various sectors. Here are some examples of real-world applications:
| Industry/sector | Example uses |
| Data centre interconnect (DCI) | Linking data centres for real-time data replication, disaster recovery and fast scaling for cloud, AI and high-performance computing (HPC) |
| Enterprise WAN | Connecting dispersed business sites and data centres with high-bandwidth, low latency links |
| Wholesale telecoms | Delivering regional and national backhaul for mobile operators, ISPs and altnets |
| AI and cloud services | Providing high-bandwidth connectivity for AI training, inference and hybrid or multi-cloud environments |
| Long-haul backbone networks | Supporting hyperscale cloud services and global enterprise applications |
| Financial services | Providing ultra-low latency links for real-time market data, trading and synchronous data replication |
| Media and broadcast | Delivering high-bandwidth, ultra-low latency links for live broadcasts and uncompressed video transport |
| Manufacturing and IIoT | Providing high‑bandwidth, low‑latency connectivity for sensor data, analytics and plant automation |
Whatever your use case, you’ll want a network you can scale as your data demands evolve.
How scalable are optical networks?
Modern optical networks are highly scalable in both capacity and reach.
To increase bandwidth, you can add more wavelengths or use the optical spectrum more efficiently. Flexible-grid DWDM lets you pack in wavelengths more densely. Coherent optical technology boosts the data rate per wavelength. And coherent pluggable modules, such as 400ZR, make it easy to boost capacity without installing new fibre.
Similarly, you can extend network reach with optical amplification and digital signal processing (DSP). EDFA and Raman amplifiers boost signals across regional and long‑haul routes, including subsea cables. Coherent DSP compensates for signal degradation, enabling high-speed data transfer over hundreds or thousands of kilometres. And with ROADMs, you can expand your network flexibly without manually reconfiguring individual nodes.
For example, our managed Optical Wavelengths services allow you to easily scale up to 400Gbps (or higher on request) across our high capacity, UK-wide fibre network. If you need more control and maximum scalability, Dark Fibre gives you almost limitless capacity and flexibility.
Optical networking solutions
At Neos Networks, we design optical networks to meet your unique business and scale as you grow. With scalable bandwidth from 10Gbps to 400Gbps across the UK, you can connect your organisation nationwide to meet the growing data demands of AI, 5G and IoT.
If you want to discuss if optical connectivity is right for your organisation, get in touch. Or download our Optical Wavelengths brochure to find out more.
Get ultrafast, low latency Optical Wavelengths
Optical networking: FAQs
-
How do optical networks support AI workloads and high-performance computing (HPC)?
Optical networks provide the high capacity, low latency transport needed to keep distributed GPU clusters synchronised for AI and HPC workloads. This consistent performance is essential for large-scale AI training and inference. -
When should you choose Dark Fibre over managed optical wavelengths (“lit fibre”)?
Choose Dark Fibre over lit fibre if you have in-house DWDM expertise and want complete control over your network. With Dark Fibre, you control the equipment, security and routing, giving you maximum flexibility and almost limitless scalability. Choose lit fibre if you need a managed service with low upfront costs, fast provisioning and predictable monthly opex. Learn more about Dark Fibre vs lit fibre. -
What’s the difference between DWDM and CWDM?
DWDM packs many tightly spaced wavelengths onto a fibre, giving much higher capacity for long‑haul transmission with amplification. CWDM uses wider wavelength spacing and supports fewer channels over shorter distances – a simpler, lower cost option for metro and enterprise links. Learn more about DWDM and CWDM. -
What’s the difference between single-mode fibre (SMF) and multi-mode fibre (MMF)?
The main difference between SMF and MMF is the core diameter and how they transmit light. SMF has a very small core (around 9µm) and carries a single light path, so it supports long-distance transmission with minimal dispersion. In contrast, MMF has a larger core (typically 50µm or 62.5µm) and supports multiple light paths. As this increases dispersion, MMF is limited to short-distance links like local area networks and building-to-building connections. -
What are coherent pluggable modules?
Coherent pluggable modules are optical transceivers that integrate high-speed optics and digital signal processing (DSP) into a single, compact unit to send data over long distances. Because they slot directly into compatible switches and routers, you can scale from 100Gbps to 400Gbps or higher by simply swapping modules, provided the host equipment supports the higher specification. This eliminates the need for bulky external hardware, saving both power and rack space as you upgrade. -
How easy is it to scale optical networks from 10Gbps to 400Gbps?
Modern optical networks are easy to scale because you can upgrade optical hardware and host equipment without replacing your underlying fibre. For example, with our Optical Wavelengths, you can increase bandwidth in simple steps from 10Gbps to 100Gbps or 400Gbps with minimal disruption. -
How secure are optical networks?
Optical networks are highly secure when deployed correctly. Unlike copper wires, fibre doesn’t emit electromagnetic signals, so optical networks are harder to tap. However, they’re not completely immune to attacks. For sensitive traffic, combining route diversity and Layer 1 encryption is recommended to reduce risk. -
What makes an optical network resilient?
A resilient network uses diverse fibre paths so traffic can be rerouted if a primary route is damaged or fails. Automatic failover mechanisms ensure traffic switches to secondary routes to maintain service if a fault or fibre breakage occurs. -
What are the typical lead times for deploying optical connectivity in the UK?
Deploying business‑grade optical connectivity typically takes 45-90 working days in the UK, depending on location, existing fibre availability and the need for wayleaves or civil construction works. But with Neos Networks' rapid activation, you can get up to 100Gbps Optical Wavelengths deployed in key UK data centres and exchanges in as little as 10 days. -
What factors influence the cost of optical networking solutions?
Optical networking costs include upfront capex like fibre installation, cables and optical hardware. Costs depend on the route design, distance and whether new fibre must be deployed or whether you can use existing infrastructure. Operational expenses include maintenance, power and ongoing support. However, with a managed service like Optical Wavelengths you can minimise upfront capex and get predictable monthly opex. With Dark Fibre, you have higher upfront capex but complete control over your network, giving you scope to minimise long-term costs.