What is 400G?
400G is the next generation of cloud infrastructure set to supercharge your business network capacity to meet ever-growing demand.
- Neos Networks
- Optical , Product interest ,

The relentless rise of cloud computing, 5G and edge-enabled networks, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI) is fuelling massive demand for ever higher data speeds and greater network efficiency.
Learn why data-hungry UK businesses are looking to 400G to scale up their network capacity and get ahead for the future.
Get ultrafast, low latency Optical Wavelengths
Supercharge your network up to 400Gbps
What is 400G?
400G is next-generation optical networking technology that can transfer data at speeds of up to 400 gigabits per second on a one optical wavelength.
While “400G”, “400GbE” and “400Gbps” are sometimes used interchangeably, they’re not the same:
- 400G typically refers to optical networking solutions that offer a 400Gbps capacity or data transfer rate on a single optical wavelength.
- 400GbE (400Gb Ethernet) is the next capacity rate for ethernet services based on the IEEE 802.3bs 400 Gigabit Ethernet standard – often interchangeable with “400G”, depending on the context.
- 400Gbps is the data transfer rate of these networks – 400 billion bits per second on a single wavelength.
How does 400G work?
400G works by combining a higher symbol rate and advanced modulation formats to boost the data transport capacity to 400Gbps on one optical wavelength. It can be used to transport either four 100GbE client services or one 400GbE client service.
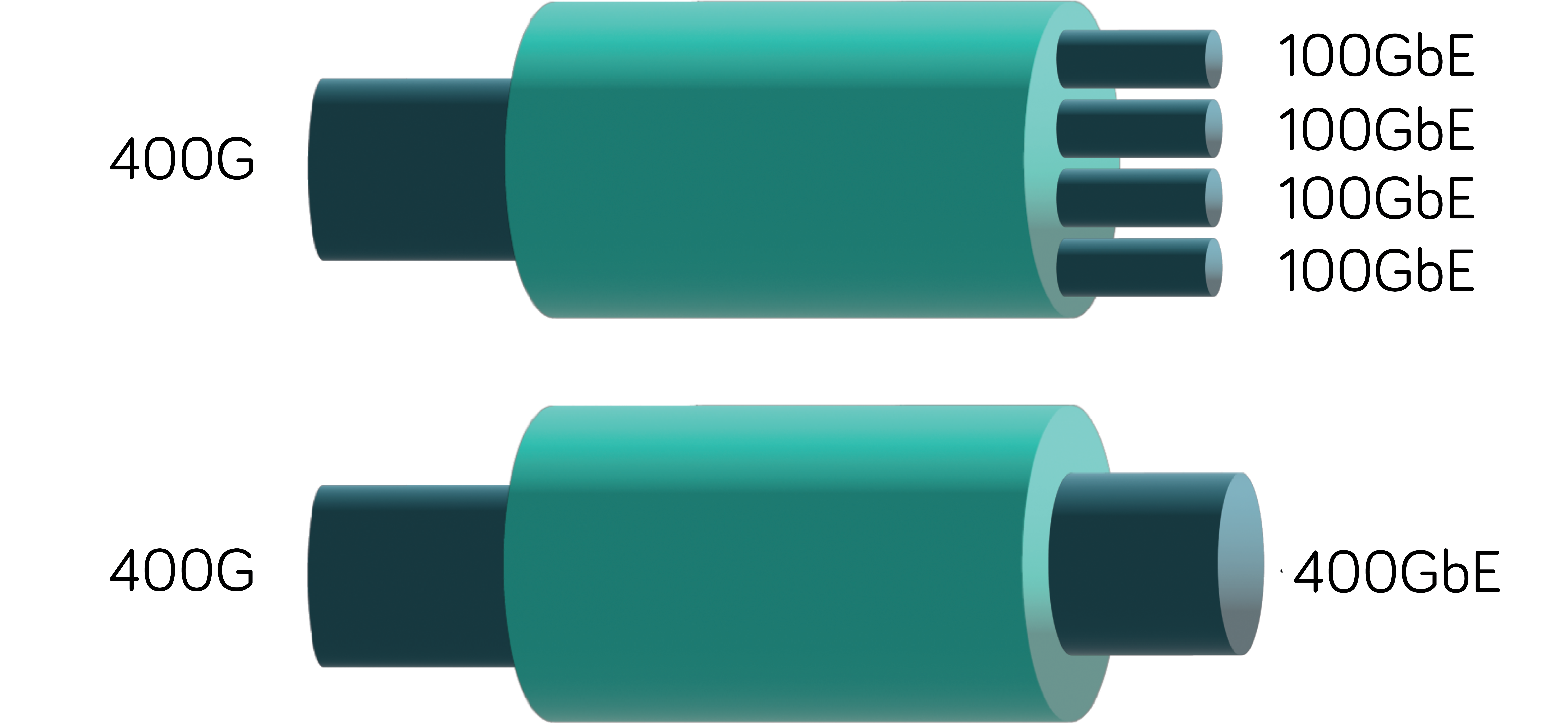
400G optical wavelength
Using a single wavelength can mean less hardware to set up and maintain, fewer points of failure, and less power and heating, all leading to lower cost per bit.
What challenges does 400G solve?
With significantly higher data transmission rates, 400G wavelengths can meet the ever-growing demand for higher network capacity in data-hungry applications like cloud computing, telecommunications, media, finance, and healthcare.
400G also allows businesses to simplify networks, increasing efficiency and transparency. But they’re not the only advantages of 400G.
What are the benefits of 400G wavelengths?
Deploying 400G optical wavelengths has several potential advantages for your business, including:
- Higher capacity: The IEEE 802.3bs 400GbE standard achieves four times faster data transfer speeds on a single wavelength.
- Cost savings: 400G simplifies your network, providing one single 400Gbps connection instead of multiple wavelengths in a bundle. Save on hardware costs and cut your cost per bit over time.
- Low latency: When correctly configured, 400G’s higher speeds and greater efficiency can mean lower latency per bit. So 400G can give you an edge, especially if data speeds are critical for your business.
- Easy scalability: The latest 400G hardware, such as high-speed optical transceivers, allows you to scale up and scale out your network architecture. Start small and transition to higher capacities as demand grows.
- Greater network transparency: By providing increased bandwidth and simplified, more advanced network infrastructure, 400G can be more transparent than previous-generation technology.
Who are 400G optical networks suitable for?
While every business will need increasing data bandwidth in future, not all need 400G right now.
400G optical networks are ideal for organisations that need to transport massive amounts of data with minimum latency and maximum reliability.
Here are some industries and sectors that can benefit from 400G now.
400G optical networks – typical applications
| Industry/sector | Example use case |
| Telecoms providers | 5G networks and high-quality streaming and video conferencing |
| Data centres | Cloud computing, data centre interconnects (DCI) and big data processing |
| Financial services | Real-time trading and transaction processing |
| Media companies | 4K video streaming and content distribution |
| Manufacturing | Real-time control of industrial operations, including the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) |
| Energy and utilities | Monitoring and managing energy infrastructure, including remote sites |
| Healthcare organisations | Sharing large medical images, patient medical histories and research data |
Is 400GbE right for your business?
If you think 400G might work for you, we can help. At Neos Networks, we design our optical networking solutions to meet your unique business needs and scale as you grow.
With Neos Networks 400Gbps Optical Wavelengths, you get:
- Flexibility: Optical wavelengths scalable from 10Gbps to 100Gbps or 400Gbps with options for multiple wavelengths between your sites
- UK-wide availability: 10Gbps and 100Gbps available from 400+ exchanges and 90+ data centres; 400Gbps from 26 UK data centres
- Reliability: Robust, ultra-high bandwidth data transfer using ROADM and DWDM technology with at least 99.85% uptime
- Route diversity: On-net and off-net routing tailored to your business for maximum resilience
- Low latency: Network engineered with the shortest hops for low or ultra-low latency
- Security: Optical protection and options for bespoke encryption
To find out more and discuss if optical networks are right for you, get in touch. We’ll be happy to help you supercharge your business network – for now and the future.
Get ultrafast, low latency Optical Wavelengths
Supercharge your network up to 400Gbps
400G optical wavelength FAQs
-
How does 400G internet speed differ from previous networking speeds, like 100G?
400G provides a data transfer rate of 400 gigabits per second (Gbps) on one optical wavelength, four times faster than 100G.
-
What are the advantages of 400G?
As 400G can deliver next-generation 400Gb Ethernet on one wavelength, potential advantages include greater network efficiency, lower latency, and enhanced flexibility and scalability.
-
What is the line rate of 400Gb Ethernet?
While the headline speed of 400GbE services is 400Gbps, the actual line rate is 425Gbps. That’s because the IEEE 802.3bs 400GbE standard includes a forward error connection (FEC) mechanism, which detects and corrects errors in transmission. The additional 25Gbps are for FEC.
-
What are the main applications or use cases for 400G?
400G is suitable for any data-intensive applications that need to transfer huge volumes of data reliably at speed. Use cases include cloud computing, data centres, media and 4K video streaming, financial services, 5G networks, AI and machine learning, and virtual and augmented reality.
-
How does 400G affect network latency and overall performance?
When designed and configured correctly, 400G optical networks can improve network latency per bit because higher data transfer rates enable faster data transmission for a given length of fibre. Similarly, 400G’s higher capacity and reduced congestion can lead to better overall performance.
You might also like

Discover our network reach
We can connect you anywhere in the UK
Great news!
"[poscode]" can be reached with our
expanded network
Speak to a representatitive to discuss your options
Contact usLearn about our prices using our online tool, LIVEQUOTE
View LIVEQUOTESorry
"[poscode]" can not be reached with our
expanded network
Speak to a representatitive to discuss your options
Contact usLearn about our prices using our online tool, LIVEQUOTE
View LIVEQUOTE



