Get ultrafast, low latency Optical Wavelengths
What is the OSI model?
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model describes how computer systems communicate across networks. Published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984, it divides communications into seven layers, providing a common basis for developing networking standards.
It’s a reference model, a conceptual framework that outlines the structure and relationship between a network’s components without prescribing specific implementation methods. It provides a universal language for network operators, developers, and students to understand, design and implement complex networks.
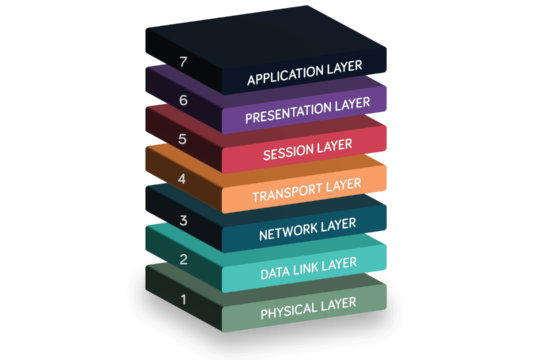
The 7 layers of the OSI model
The OSI model organises network communications into a stack of seven layers:
- The Physical Layer
- The Data Link Layer
- The Network Layer
- The Transport Layer
- The Session Layer
- The Presentation Layer
- The Application Layer
Each layer performs a specific function and interacts with the layers above and below, ensuring efficient data transmission. Typically, the layers are listed from top to bottom (7 to 1) to reflect the data flow during communication, starting from the user’s application at the Application Layer and moving down to the Physical Layer.
7 layers of the OSI model
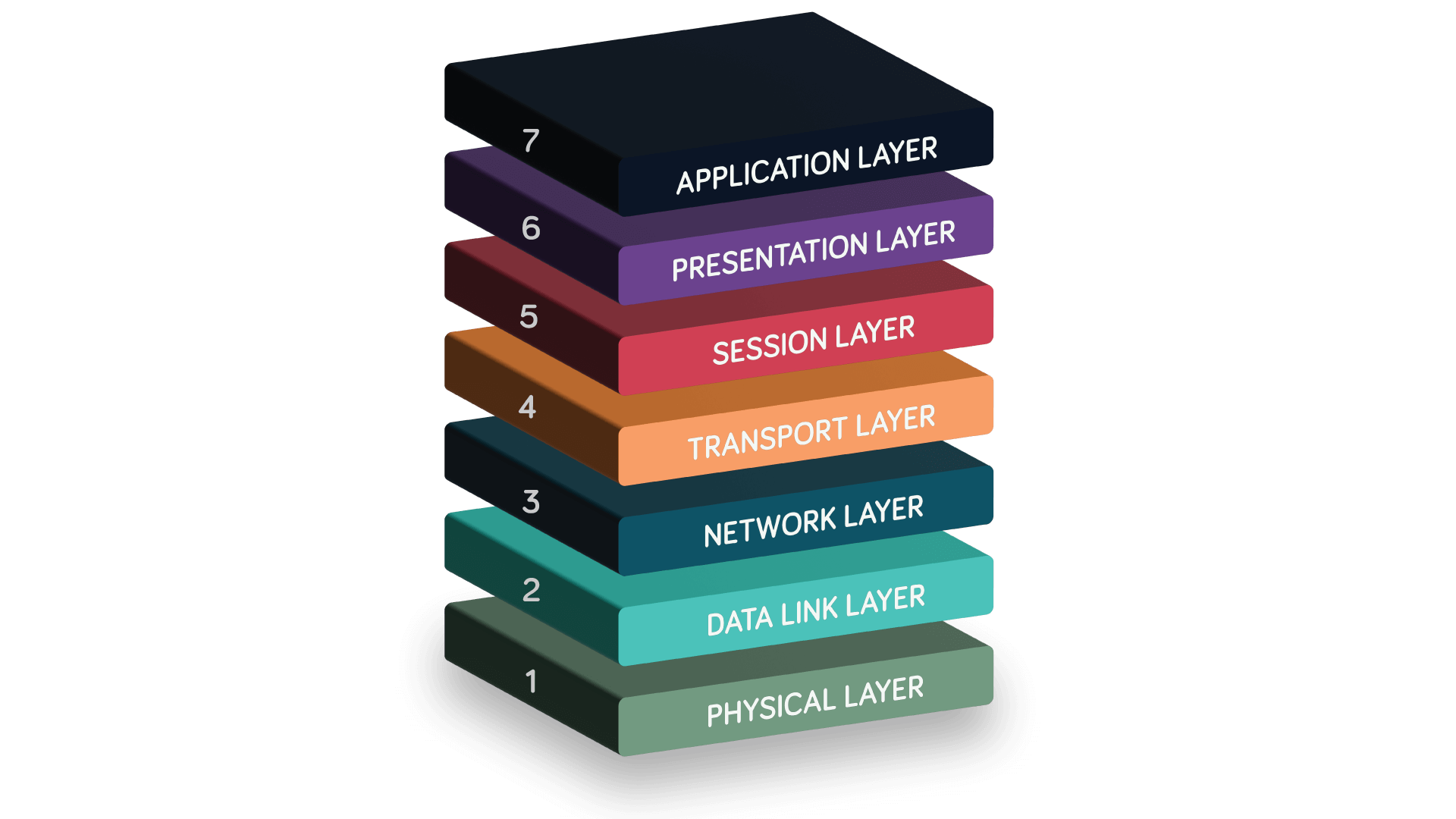
Here’s a breakdown of the seven layers and their roles in a network.
7 layers explained
| # | Layer | Function |
| 7 | Application Layer | Interacts directly with end users through applications like email clients and browsers. It includes protocols like SMTP for email, HTTP for web browsing and FTP for file transfers. |
| 6 | Presentation Layer | Translates data between the Application Layer and the lower layers. This includes data formatting, encryption and compression. |
| 5 | Session Layer | Starts, maintains and ends connections between devices. It also coordinates data exchange and synchronisation. |
| 4 | Transport Layer | Uses transport protocols like TCP and UDP to transfer data between end systems. It divides data from the Session Layer into segments, ensuring flow control and error correction. |
| 3 | Network Layer | Handles the routing of data across multiple networks, determining the optimal path for transmission. Protocols like the Internet Protocol (IP) break data into packets and use IP addresses to deliver them to their destination. |
| 2 | Data Link Layer | Manages communication between physically connected nodes on a network. It packages data from the Network Layer into frames and ensures reliable transfer between devices over the physical medium. |
| 1 | Physical Layer | Transmits and receives raw data (ones and zeros) as electrical signals, light pulses or radio waves over physical media. It includes hardware like cables, fibre optic equipment and wireless transmitters or antennas. |
How does the OSI model work?
When data is transmitted over a network, it moves sequentially through the seven layers, from the Application Layer at the top to the Physical Layer at the bottom.
For example, here’s what happens when you send an email:
- You write a message in an email app like Gmail or Outlook and click “send”. The email client uses a protocol like SMTP to process your message (Application Layer).
- The email client formats your message for transmission, including encryption if enabled (Presentation Layer).
- A session is established between your device and the email server to manage the ongoing data exchange (Session Layer).
- The email data is divided into smaller segments for transmission, and protocols like TCP and UDP ensure they’re delivered reliably (Transport Layer).
- The email segments are assigned source and destination IP addresses to be routed across the network (Network Layer).
- The IP packets are encapsulated into frames to be transmitted over the local network (Data Link Layer).
- The frames are converted into electrical, optical, or wireless signals and transmitted through a physical medium like a network cable or Wi-Fi (Physical Layer).
At the receiving end, the process is reversed: the data travels up from the Physical Layer to the Application Layer, reconstructing the email for its recipient.
OSI model vs TCP/IP model
Another significant networking framework is the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol model (TCP/IP), also known as the Internet Protocol Suite. Unlike the OSI model, which is primarily theoretical, TCP/IP is a practical framework designed specifically for implementing internet communications.
Initially developed for the US military’s ARPANET, the forerunner of the internet, the TCP/IP model consists of just four layers:
- The Application Layer combines the functions of OSI’s Application, Presentation and Session layers, managing high-level protocols and user interactions.
- The Transport Layer uses protocols like TCP and UDP to ensure data transfer between end systems, like OSI’s Transport Layer.
- The Internet Layer manages addressing and routing using the Internet Protocol, like OSI’s Network Layer.
- The Link Layer handles data transmission over physical media, like cables and Wi-Fi, combining the functions of OSI’s Physical and Data Link layers.
OSI model vs TCP/IP model: comparing layers
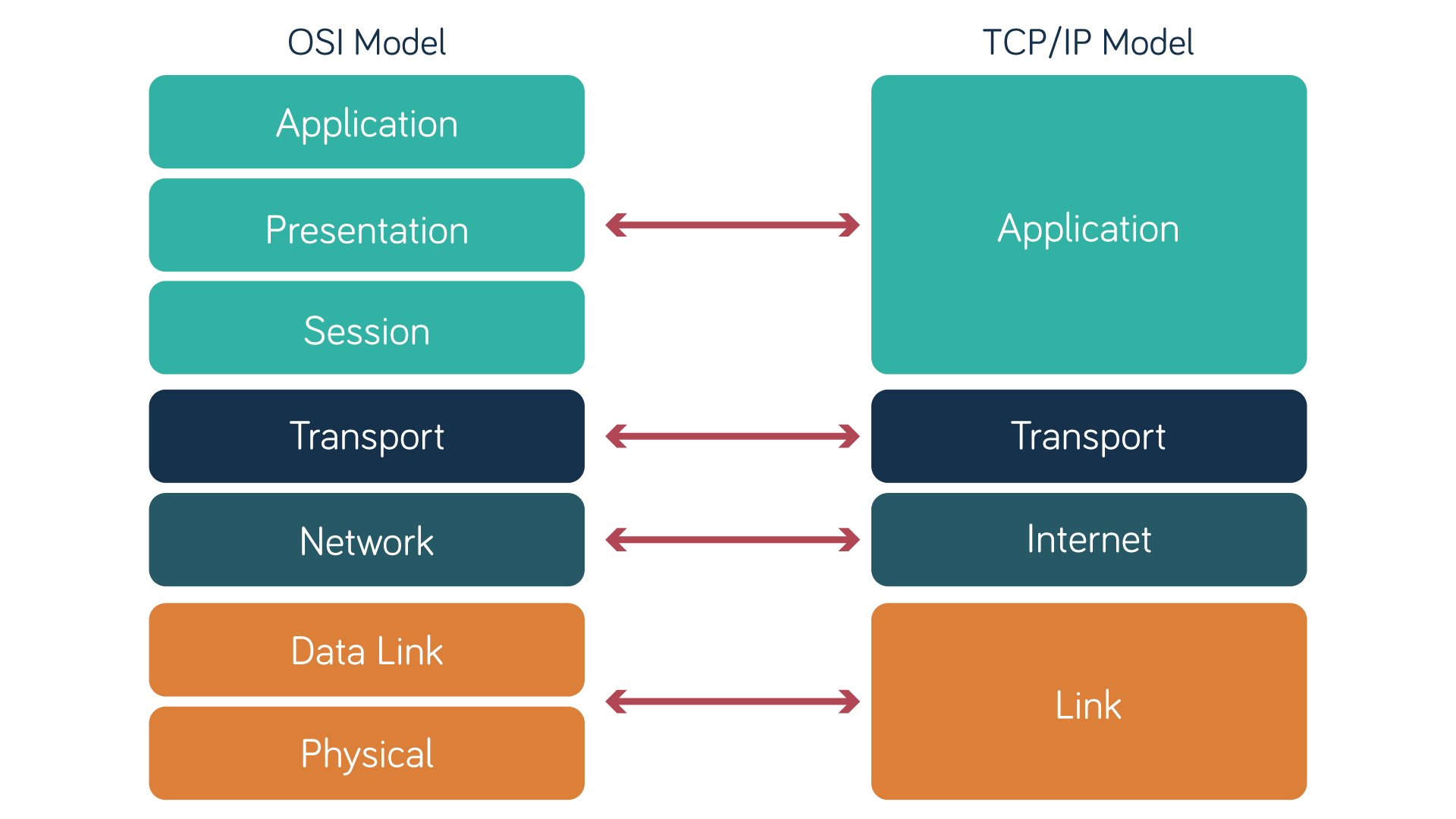
Here’s a summary of the main differences between the two:
| Feature | OSI model | TCP/IP model |
| Layers | Seven: Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link and Physical | Four: Application, Transport, Internet and Link |
| Development | Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) | Originally developed by the US Department of Defence (ARPANET) and maintained today by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) |
| Use | A reference model used to standardise general network communications | A practical model used to implement internet communications |
In short, the OSI model is a comprehensive theoretical framework that standardises network communications without relying on specific protocols. In contrast, TCP/IP is a simpler, practical model that defines and supports the implementation of internet protocols.
While the TCP/IP model is more widely used in practice because it underpins the internet, the OSI model remains significant.
Why is the OSI model important?
Although theoretical, the OSI model provides a detailed understanding of fundamental network architecture, making it valuable for several reasons:
- Standardisation and interoperability: The model provides a universal framework, promoting the development of interoperable protocols and devices.
- Troubleshooting and security: The multi-layered structure allows administrators to identify and fix technical or security failures in their specific layers without disrupting the others.
- Education and design: It’s a foundational model for IT professionals and students to share knowledge about network architecture and adapt networks for the future.
OSI model disadvantages
Despite its value, the OSI model has its limitations. First, real-world networking technologies don’t always fit neatly into its framework, and the functions of its layers can sometimes overlap in practice.
In addition, its comprehensive nature can make it overly complex for practical use. The simpler, more practical TCP/IP model has largely supplanted the OSI model, especially for internet communications.
However, the OSI model remains a fundamental theoretical framework. Whether you're a network professional, student, or tech enthusiast, it provides valuable insight into the complex world of computer networking.
Making connectivity work
At Neos Networks, we use the OSI model to visualise complex networks and make connectivity work for businesses across the UK.
For example, optical wavelengths operate in the Physical Layer (layer 1), enabling high-bandwidth data transmission across fibre optic networks. In contrast, Ethernet primarily functions at the Data Link Layer (layer 2) but also defines standards for some layer 1 components, like cables and connectors.
If you’re looking to supercharge your business with high capacity connectivity for the future, get in touch. We’ll be happy to make connectivity work for you.